Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Insight and Action
Related Articles: Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Insight and Action
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Insight and Action. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Insight and Action
In the contemporary data-driven landscape, dashboards have emerged as indispensable tools for organizations seeking to glean meaningful insights from vast quantities of information. A well-designed dashboard transcends mere data visualization; it serves as a dynamic window into key performance indicators (KPIs), trends, and patterns, empowering informed decision-making. This comprehensive guide explores the essential principles and best practices for crafting effective dashboards that deliver impactful value.
Understanding the Purpose and Audience:
The foundation of a successful dashboard lies in its clear purpose and target audience. Before embarking on the design process, it is crucial to define the specific goals the dashboard aims to achieve. Is it intended to monitor real-time performance, track progress against objectives, identify potential issues, or facilitate strategic planning? Once the purpose is established, the target audience must be considered. Who will be interacting with the dashboard, and what level of technical expertise do they possess? Tailoring the dashboard’s content, visual style, and level of detail to the audience’s needs is paramount.
Selecting the Right Data and KPIs:
Data selection is a critical step in dashboard creation. The chosen data must be relevant to the defined purpose and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. The dashboard should focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide a concise and actionable overview of performance. KPIs should be measurable, specific, and aligned with the desired outcomes. For instance, a sales dashboard might display KPIs such as revenue, conversion rate, and average order value.
Choosing an Appropriate Visualization Style:
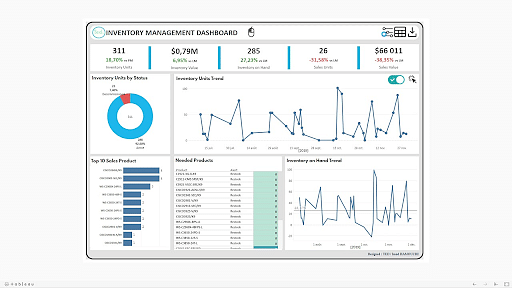
The choice of visualization style plays a pivotal role in conveying data effectively. Different visualization types excel in representing various data types and patterns. Common visualization techniques include:
- Line Charts: Ideal for showcasing trends over time, particularly for continuous data.
- Bar Charts: Effective for comparing categorical data, such as sales by product category.
- Pie Charts: Suitable for illustrating proportions of a whole, such as market share distribution.
- Scatter Plots: Useful for identifying relationships and correlations between two variables.
- Maps: Effective for visualizing geographical data, such as sales by region.
- Gauges: Ideal for displaying real-time performance against targets, such as website traffic or customer satisfaction.
The selection of visualization types should be driven by the data being presented and the insights intended to be communicated.
Prioritizing Clarity and Simplicity:
A well-designed dashboard prioritizes clarity and simplicity, ensuring that the information is easily understood and readily interpreted. Avoid overwhelming the user with excessive data or complex visualizations. Instead, focus on presenting the most critical information in a concise and digestible manner. Utilize clear and concise labels, legends, and annotations to enhance understanding.
Ensuring Interactivity and Drill-Down Capabilities:
Interactivity is a key feature of effective dashboards, allowing users to explore the data in greater depth. Interactive elements such as filters, drill-down capabilities, and dynamic updates empower users to investigate specific areas of interest and gain deeper insights. For instance, a user might filter sales data by region or product category, or drill down into individual customer profiles for further analysis.
Maintaining Consistency and Branding:
Consistency in design and branding enhances the dashboard’s usability and professionalism. Utilizing a consistent color palette, font styles, and visual elements creates a cohesive and visually appealing experience. Integrating the organization’s branding guidelines ensures that the dashboard aligns with the company’s overall identity.
Optimizing for Mobile Devices:
In today’s mobile-first world, it is crucial to ensure that dashboards are accessible and user-friendly on various devices. Responsive design principles should be employed to ensure that the dashboard adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and orientations. This enhances accessibility and allows users to access the information they need regardless of their device.
Implementing Data Security and Access Control:
Data security and access control are paramount for dashboards that handle sensitive information. Implementing robust security measures, such as user authentication and role-based access control, ensures that only authorized personnel can access and manipulate the data. This safeguards sensitive information and maintains data integrity.
Monitoring and Iterating:
Dashboard creation is an iterative process. Once the initial dashboard is deployed, it is essential to monitor its usage and effectiveness. Gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and refine the dashboard’s design and functionality. Regularly review and update the dashboard to ensure that it remains relevant and provides valuable insights.
FAQs on Crafting Effective Dashboards:
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a dashboard?
A: Common mistakes include:
- Overloading the dashboard with too much data.
- Using overly complex or confusing visualizations.
- Failing to provide clear and concise labels and annotations.
- Ignoring user needs and preferences.
- Neglecting to test and iterate on the dashboard’s design.
Q: How can I ensure that my dashboard is user-friendly?
A: User-friendliness can be achieved by:
- Prioritizing clarity and simplicity in design.
- Using intuitive navigation and interactions.
- Providing clear and concise explanations of data points and visualizations.
- Testing the dashboard with target users to gather feedback.
Q: What tools can I use to create dashboards?
A: There are numerous tools available for dashboard creation, including:
- Microsoft Power BI: A comprehensive business intelligence platform with powerful data visualization and analysis capabilities.
- Tableau: A popular data visualization tool known for its intuitive interface and drag-and-drop functionality.
- Google Data Studio: A free and user-friendly tool for creating interactive dashboards.
- Qlik Sense: A data discovery platform that empowers users to explore data and uncover hidden insights.
Tips for Creating Effective Dashboards:
- Start with a clear purpose and target audience.
- Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide actionable insights.
- Choose visualization types that best represent the data and communicate the desired insights.
- Prioritize clarity and simplicity in design.
- Incorporate interactivity and drill-down capabilities to enhance data exploration.
- Maintain consistency in design and branding.
- Optimize for mobile devices to ensure accessibility.
- Implement data security and access control measures.
- Monitor and iterate on the dashboard’s design based on user feedback.
Conclusion:
Crafting effective dashboards is an essential skill for organizations seeking to leverage data for informed decision-making. By adhering to the principles outlined in this guide, organizations can create dashboards that provide clear, concise, and actionable insights, empowering them to achieve their strategic goals. Remember, a good dashboard is not merely a collection of data points; it is a powerful tool that transforms data into knowledge and action. By focusing on the user’s needs, prioritizing clarity and simplicity, and iterating on the design, organizations can create dashboards that deliver real value and drive positive outcomes.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Insight and Action. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!