Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Action
Related Articles: Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Action
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Action. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Action
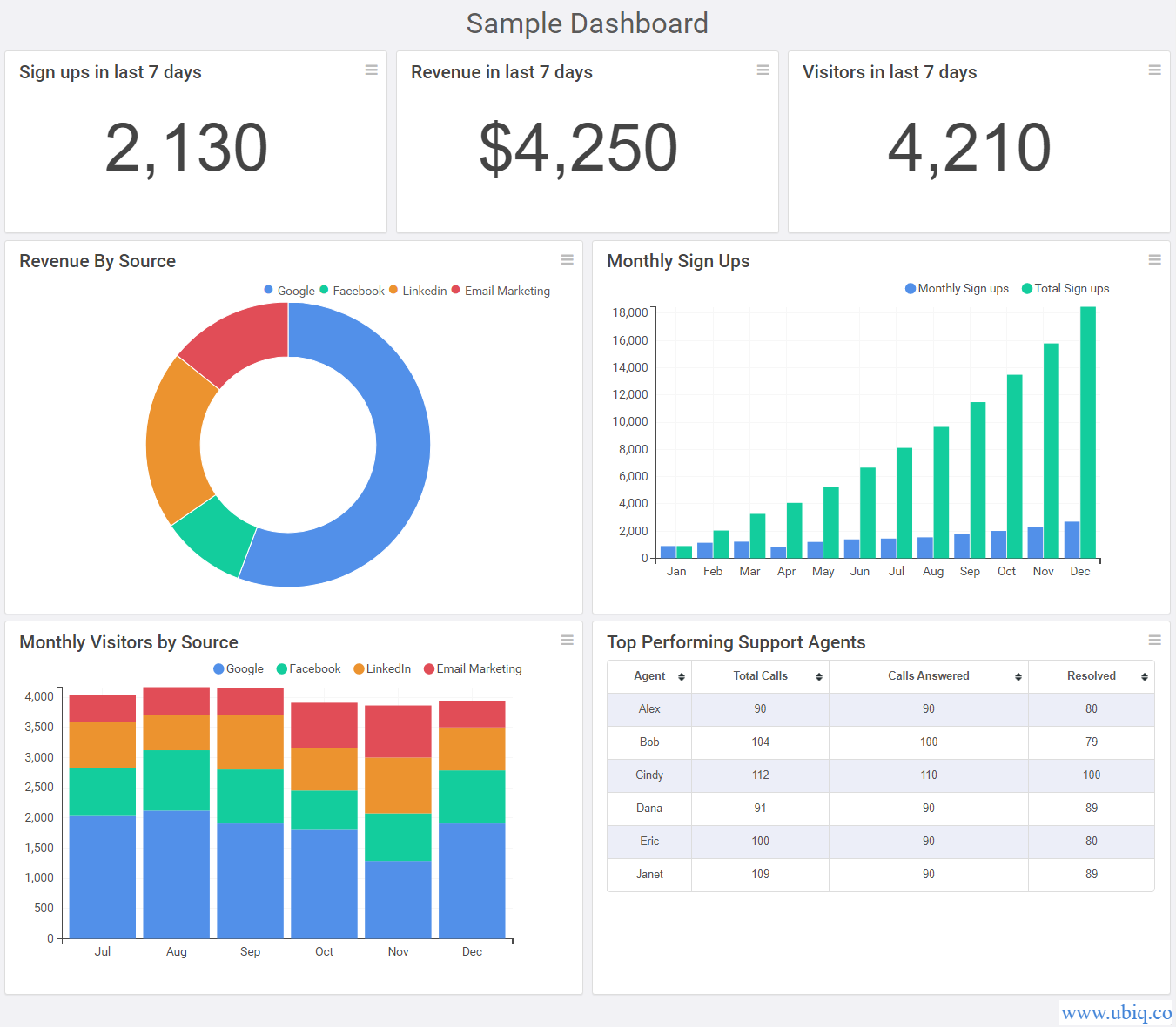
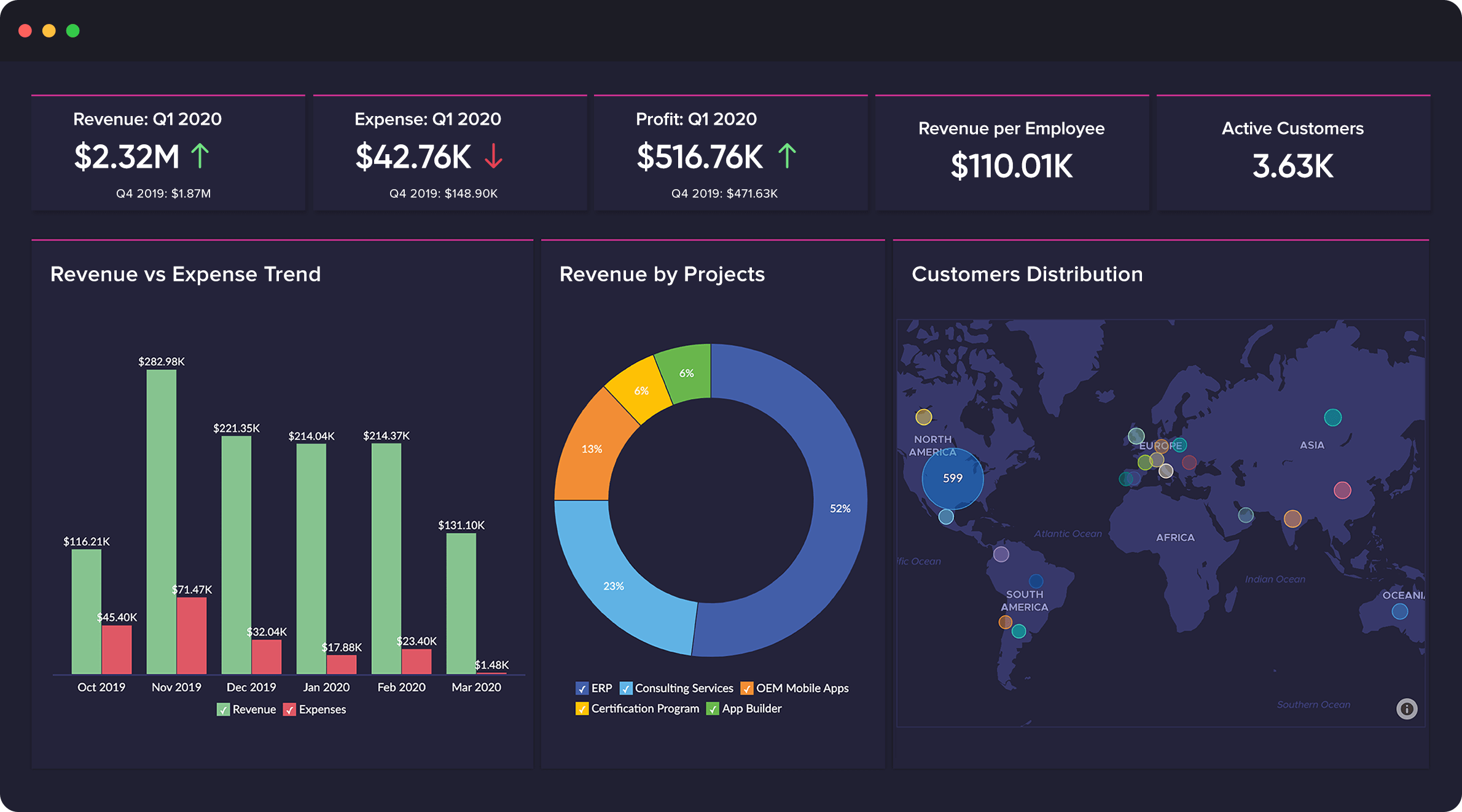
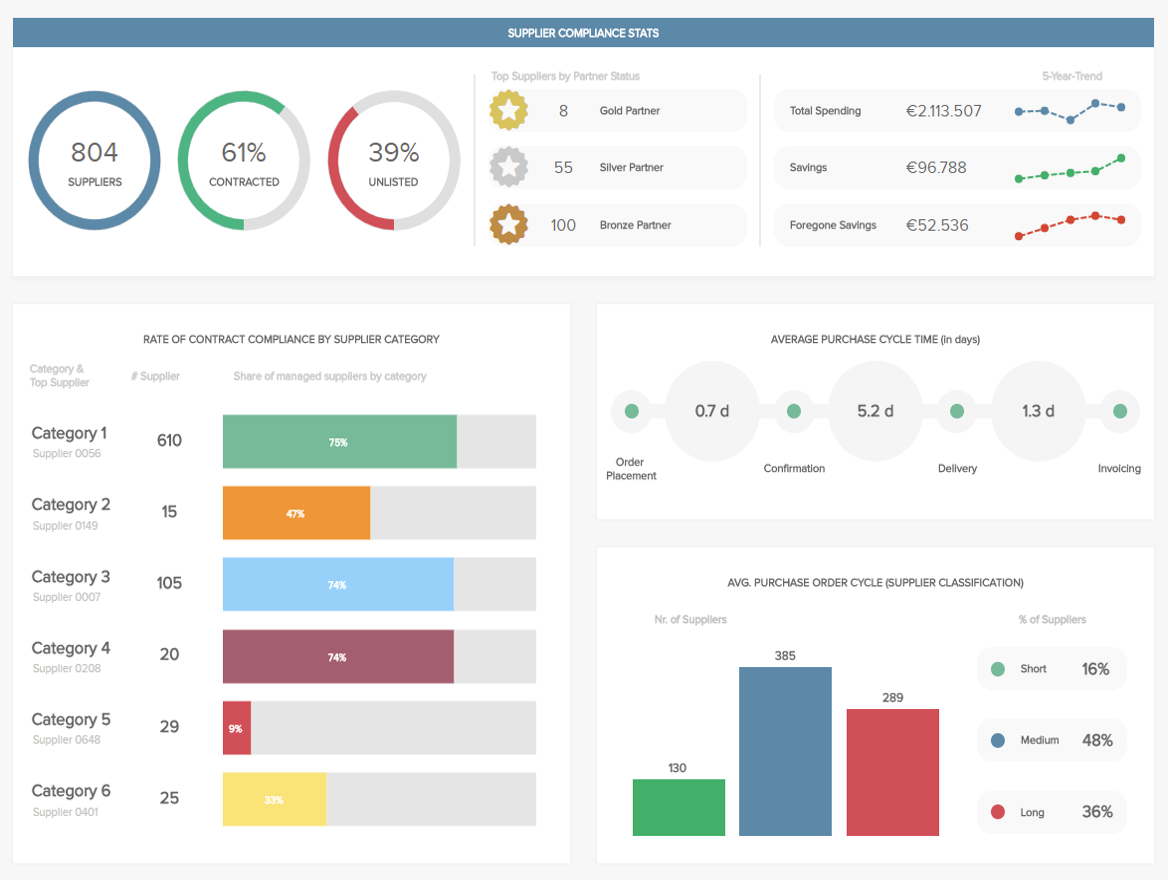
In the modern data-driven world, dashboards have become indispensable tools for organizations seeking to make informed decisions. These interactive visual displays present critical information in a clear and concise manner, enabling users to quickly grasp trends, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. However, crafting an effective dashboard goes beyond simply displaying data; it requires a strategic approach that prioritizes clarity, relevance, and user experience. This guide explores the key principles and practices for designing dashboards that empower users to understand and act upon data insights.
Understanding the Purpose and Audience:
The first step in dashboard design is to clearly define its purpose and intended audience. This crucial step sets the foundation for all subsequent design decisions.
- Define the Goal: What specific insights should the dashboard convey? Is it intended for monitoring performance, identifying opportunities, or troubleshooting issues? A well-defined goal ensures the dashboard focuses on the most critical information.
- Identify the Audience: Who will be using the dashboard? Understanding the user’s role, technical expertise, and data literacy is essential for tailoring the design to their needs. For instance, a dashboard for executives might prioritize high-level summaries and key performance indicators (KPIs), while a dashboard for analysts might require more detailed data and granular insights.
Choosing the Right Visualizations:
Effective dashboards leverage a variety of visualizations to present data in a compelling and understandable manner. The choice of visualization depends on the type of data and the message being conveyed.
- Line Charts: Ideal for showcasing trends over time, highlighting growth, decline, or cyclical patterns.
- Bar Charts: Effective for comparing discrete categories, illustrating differences in values, and highlighting rankings.
- Pie Charts: Useful for representing proportions and part-to-whole relationships, but should be used sparingly as they can become cluttered with too many categories.
- Scatter Plots: Show the relationship between two variables, revealing correlations and outliers.
- Maps: Visually represent geographical data, highlighting regional trends or variations.
- Heatmaps: Display data density or intensity across a matrix, revealing areas of high or low activity.
Prioritizing Clarity and Simplicity:
A well-designed dashboard prioritizes clarity and simplicity, ensuring information is readily accessible and digestible.
- Minimalist Design: Avoid overwhelming the user with too much information. Prioritize the most essential data points and present them in a clear and concise manner.
- Visual Hierarchy: Use size, color, and positioning to guide the user’s attention towards the most important elements. A clear hierarchy helps users quickly identify key insights and understand the relative importance of different data points.
- Consistent Design: Maintain a consistent visual language throughout the dashboard, using a consistent color scheme, font style, and layout. This creates a cohesive and user-friendly experience.
Ensuring Interactivity and Exploration:
Interactive elements enhance the user experience and empower users to explore the data in greater depth.
- Filtering and Sorting: Allow users to filter data based on specific criteria and sort it by various parameters, enabling them to focus on the information most relevant to their needs.
- Drill-Down Functionality: Enable users to delve deeper into specific data points by providing drill-down options, allowing them to investigate underlying details and uncover hidden insights.
- Data Exploration Tools: Provide users with tools to interact with the data directly, such as adding annotations, highlighting trends, and creating custom visualizations.
Measuring and Iterating:
Dashboard design is an iterative process that requires ongoing evaluation and refinement.
- User Feedback: Gather feedback from users on their experience with the dashboard, identifying areas for improvement and ensuring the design meets their needs.
- Analytics Tracking: Monitor user interactions with the dashboard, analyzing which elements are most frequently accessed and which areas require further clarification.
- Continuous Improvement: Use feedback and analytics data to iteratively refine the dashboard design, ensuring it remains effective and relevant.
FAQs about Dashboard Design:
1. What are the most common mistakes in dashboard design?
- Overloading the dashboard with too much information.
- Using overly complex visualizations that are difficult to understand.
- Failing to consider the needs and data literacy of the target audience.
- Neglecting to provide context for the data presented.
- Ignoring the importance of interactivity and exploration.
2. How can I choose the right visualizations for my dashboard?
- Consider the type of data being presented.
- Determine the message you want to convey.
- Choose visualizations that are appropriate for the intended audience.
- Prioritize clarity and simplicity over visual complexity.
3. What are some best practices for creating interactive dashboards?
- Provide filtering and sorting options to allow users to customize their view of the data.
- Enable drill-down functionality to allow users to explore specific data points in greater detail.
- Include data exploration tools that empower users to interact with the data directly.
4. How can I ensure my dashboard is accessible to all users?
- Use clear and concise language.
- Provide alternative text descriptions for images and charts.
- Ensure the dashboard is compatible with assistive technologies.
- Test the dashboard with users with disabilities to identify any accessibility issues.
5. How can I measure the effectiveness of my dashboard?
- Track user engagement and interactions.
- Gather feedback from users on their experience.
- Analyze the impact of the dashboard on decision-making.
- Continuously iterate and improve the design based on data and feedback.
Tips for Effective Dashboard Design:
- Start with a clear understanding of the purpose and audience.
- Prioritize the most essential data points and present them in a clear and concise manner.
- Use a variety of visualizations to effectively convey different types of data.
- Maintain a consistent visual language throughout the dashboard.
- Include interactive elements that empower users to explore the data.
- Gather user feedback and continuously iterate on the design.
Conclusion:
Crafting an effective dashboard requires a strategic approach that prioritizes clarity, relevance, and user experience. By understanding the purpose and audience, selecting appropriate visualizations, prioritizing simplicity and interactivity, and continuously measuring and iterating, organizations can create dashboards that empower users to make informed decisions based on data insights. These dashboards serve as powerful tools for driving business performance, identifying opportunities, and making informed decisions in a data-driven world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Guide to Visualizing Data for Action. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!