Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization
Related Articles: Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization
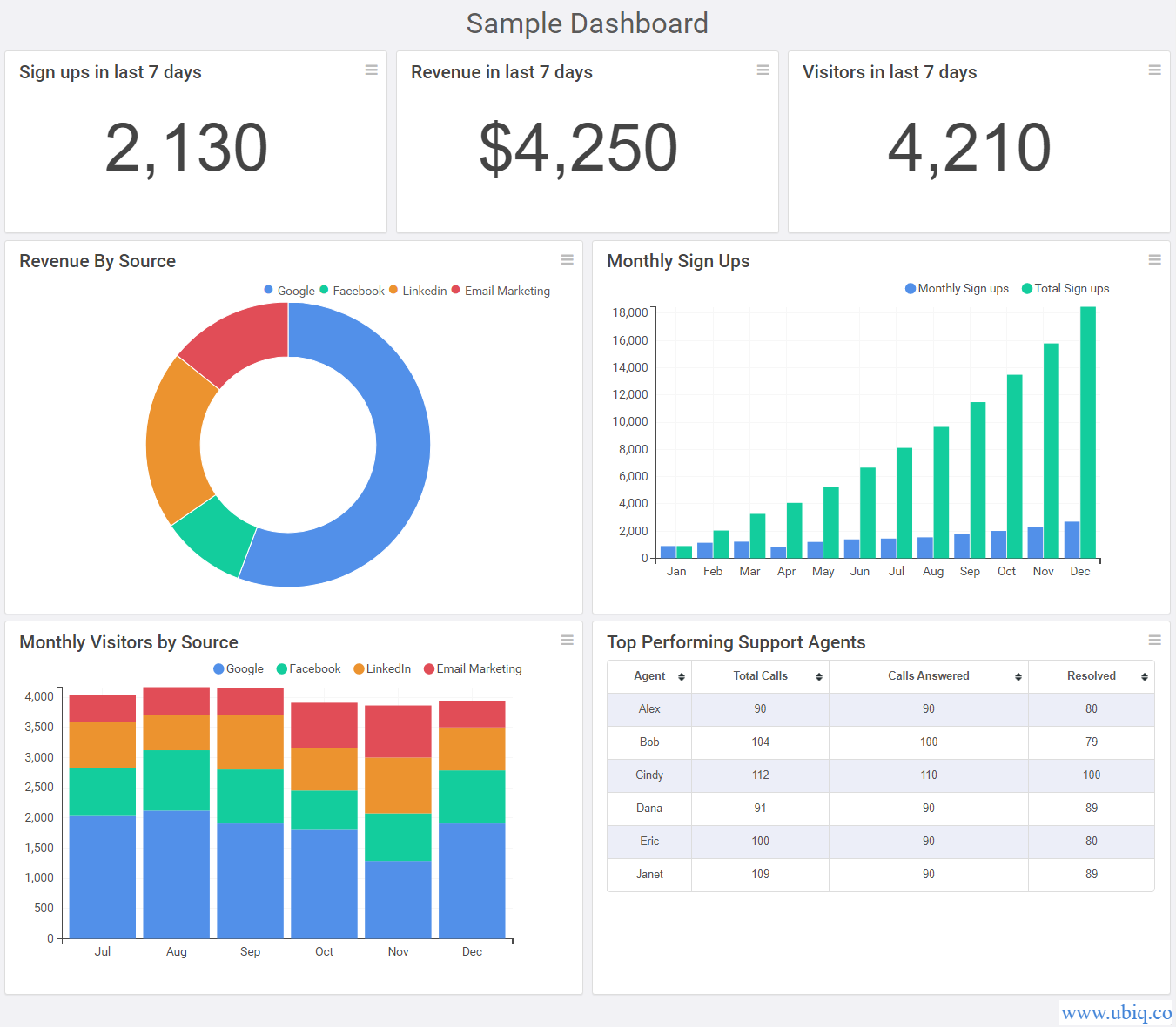
In the contemporary landscape of data-driven decision-making, the ability to effectively visualize and interpret information is paramount. Dashboards, acting as the visual interface for data, play a crucial role in transforming raw data into actionable insights. This guide delves into the intricacies of dashboard design, providing a comprehensive understanding of the principles and best practices that contribute to creating compelling and informative data visualizations.
Understanding the Essence of a Dashboard
At its core, a dashboard serves as a centralized hub for presenting key performance indicators (KPIs) and relevant data in a visually appealing and readily digestible format. It facilitates informed decision-making by offering a succinct overview of critical metrics, trends, and anomalies, enabling users to quickly grasp the current state and trajectory of various processes and operations.
The Importance of a Well-Designed Dashboard
A well-designed dashboard goes beyond simply presenting data; it fosters a deeper understanding of the underlying information, driving meaningful actions. Its significance lies in:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By distilling complex data into clear visuals, dashboards empower users to make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
- Improved Communication: Dashboards act as a common language for communicating data across teams and departments, fostering alignment and transparency.
- Streamlined Monitoring: Regularly updated dashboards enable continuous monitoring of key metrics, facilitating proactive identification and resolution of potential issues.
- Increased Efficiency: By providing a centralized view of relevant information, dashboards eliminate the need for time-consuming data gathering and analysis, fostering efficiency in decision-making processes.
- Data-Driven Culture: Well-designed dashboards encourage a data-driven culture within organizations, promoting data-informed decision-making at all levels.
Key Elements of a Successful Dashboard
The effectiveness of a dashboard hinges on its ability to present information in a clear, concise, and engaging manner. This involves carefully considering the following key elements:
1. Defining the Target Audience and Objectives
The design of a dashboard must align with the specific needs and objectives of its intended audience. This involves understanding:
- User Roles: Who will be using the dashboard? What are their responsibilities and decision-making authority?
- Data Requirements: What specific data points are crucial for the target audience to effectively monitor and analyze?
- Desired Outcomes: What actions do you want to encourage or facilitate through the dashboard?
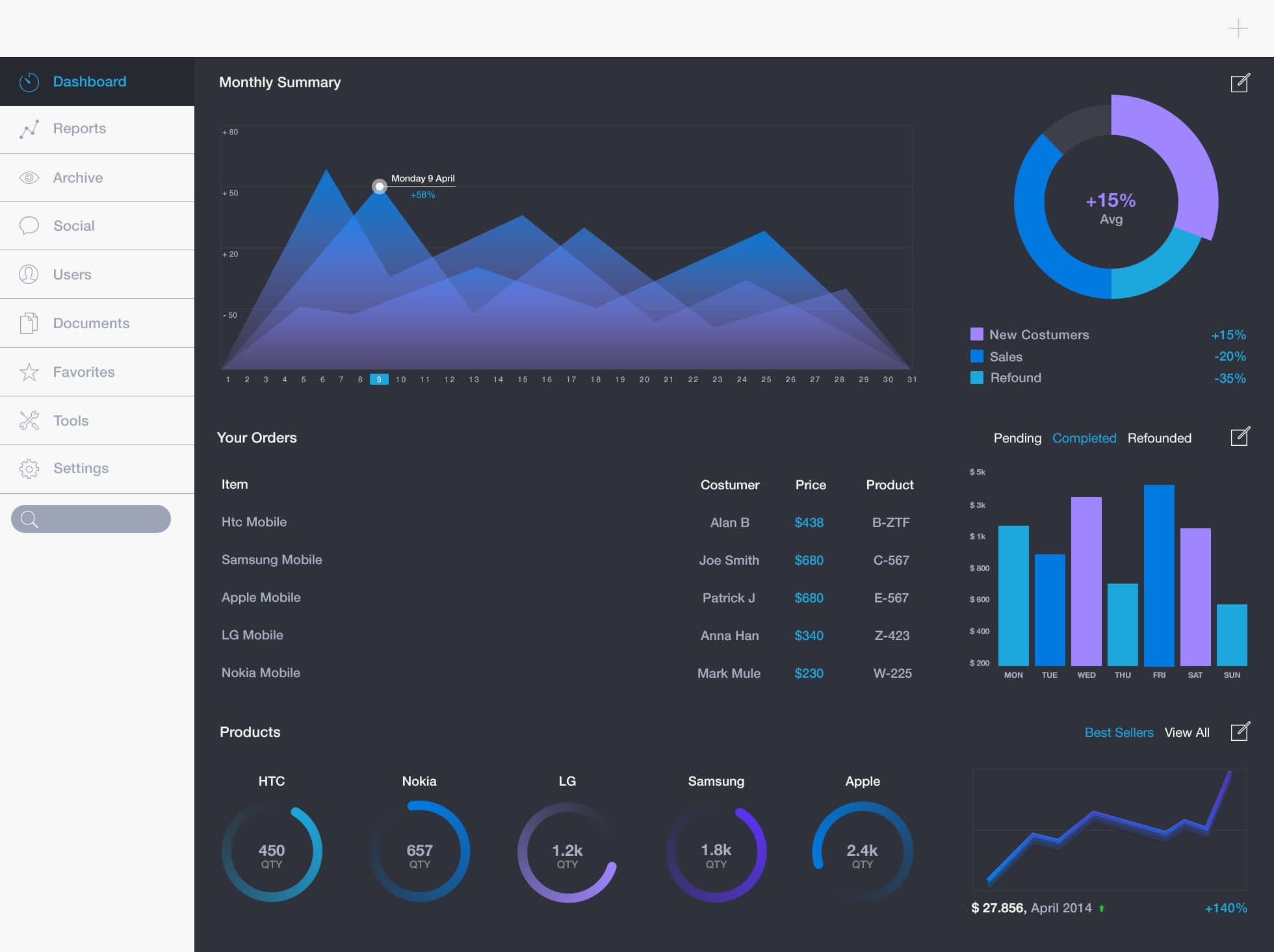
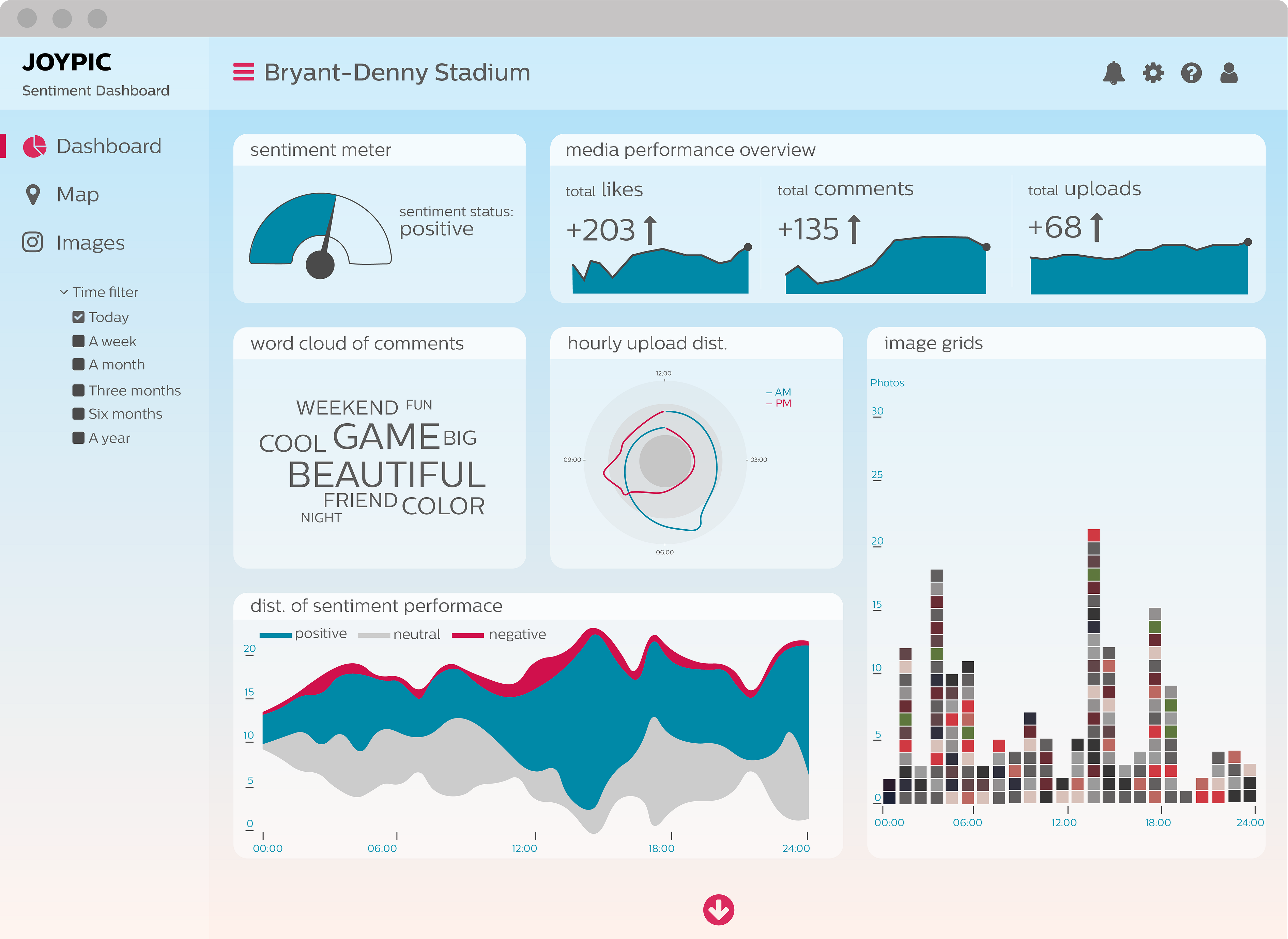
2. Choosing the Right Visualizations
The selection of appropriate visualizations is crucial for effectively communicating data. Different chart types excel at conveying specific types of information:
- Line Charts: Ideal for showcasing trends over time, highlighting patterns and identifying anomalies.
- Bar Charts: Effectively compare discrete categories, revealing differences in magnitude or frequency.
- Pie Charts: Represent proportions of a whole, useful for illustrating relative contributions.
- Scatter Plots: Show relationships between two variables, revealing correlations and outliers.
- Maps: Visually depict geographic data, highlighting regional variations and trends.
- Gauges: Display a single metric against a target or threshold, providing a clear visual indication of performance.
3. Prioritizing Key Metrics and Data Points
The dashboard should focus on presenting the most critical information, avoiding overwhelming the user with unnecessary details. This involves:
- Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): These are the most important metrics that reflect the overall performance and success of the initiative or process.
- Prioritizing Data Points: Select only the data points that directly contribute to the understanding and analysis of the KPIs.
- Limiting the Number of Visualizations: Keep the number of charts and graphs to a manageable level, avoiding information overload.
4. Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency
The foundation of a reliable dashboard lies in the accuracy and consistency of the underlying data. It is essential to:
- Validate Data Sources: Ensure that the data used is accurate, reliable, and from trusted sources.
- Maintain Data Consistency: Establish a standardized data format and ensure that data is consistently formatted across different sources.
- Implement Data Quality Checks: Regularly review data for inconsistencies, errors, and outliers.
5. Emphasizing Clarity and Readability
The design of the dashboard should prioritize clarity and readability, ensuring that information is easily understood and interpreted. Key considerations include:
- **Clear Labels and


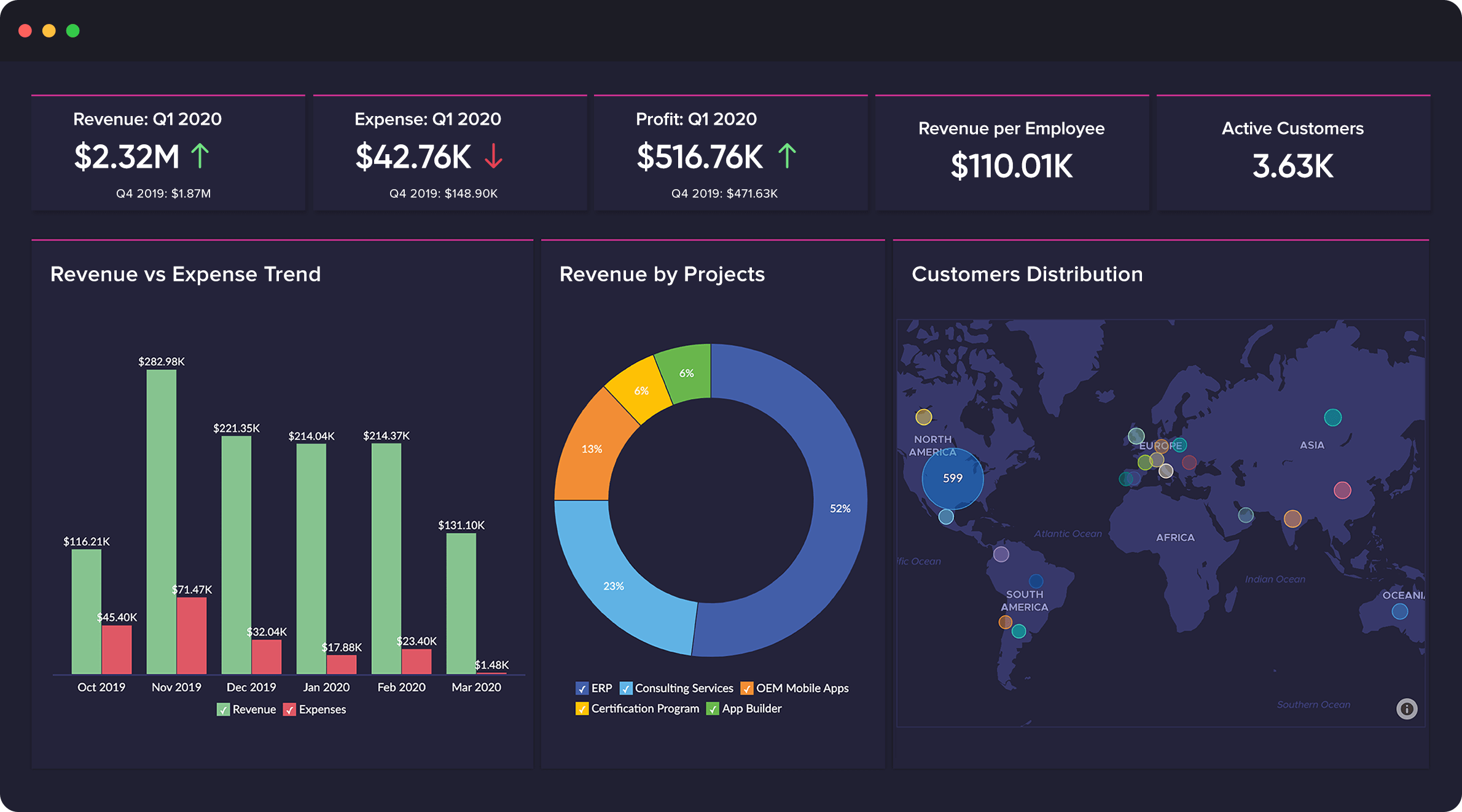

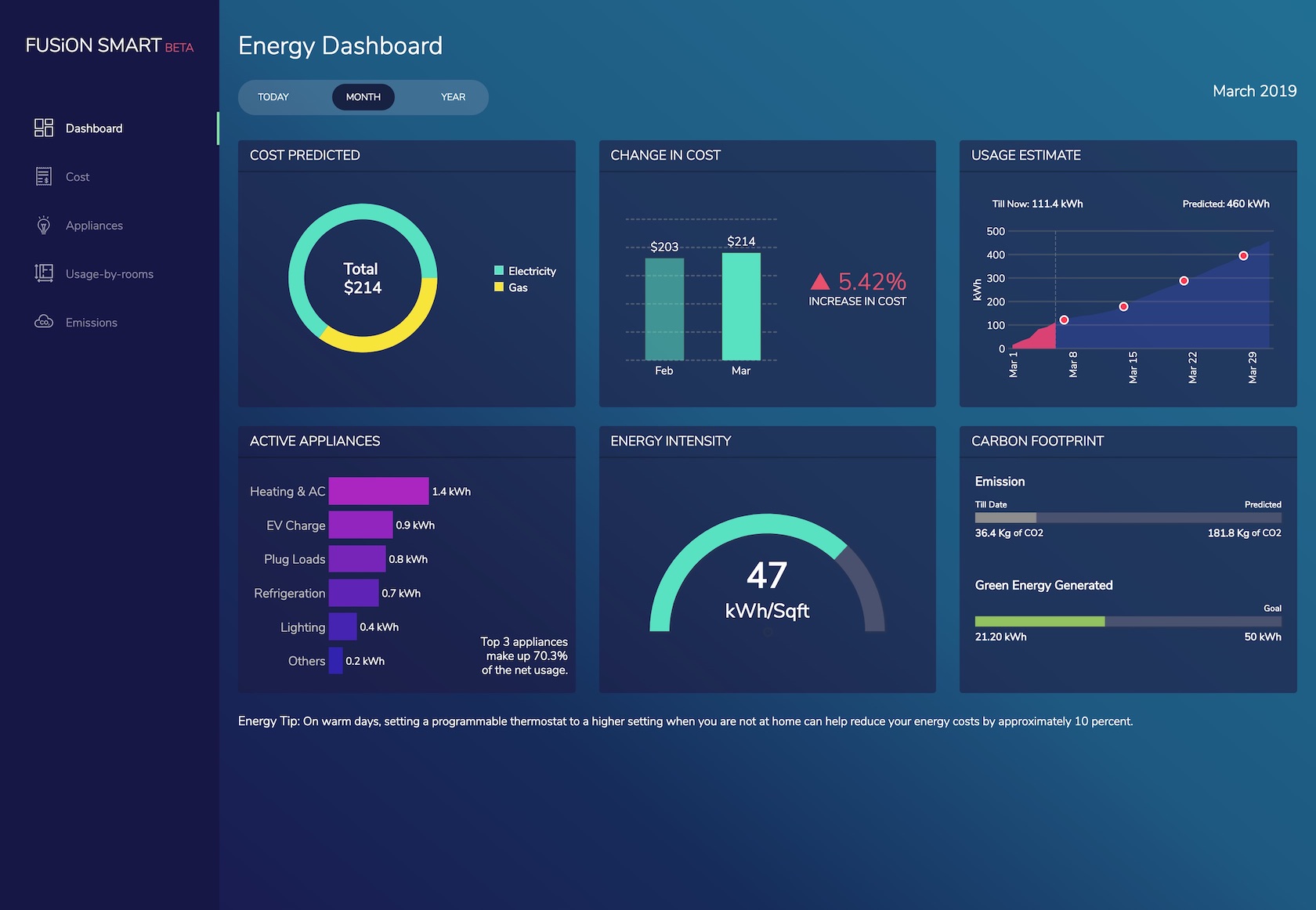
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Crafting Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Visualization. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!