Crafting a Custom Dashboard: A Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Your Data
Related Articles: Crafting a Custom Dashboard: A Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Your Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Crafting a Custom Dashboard: A Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Your Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Crafting a Custom Dashboard: A Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Your Data
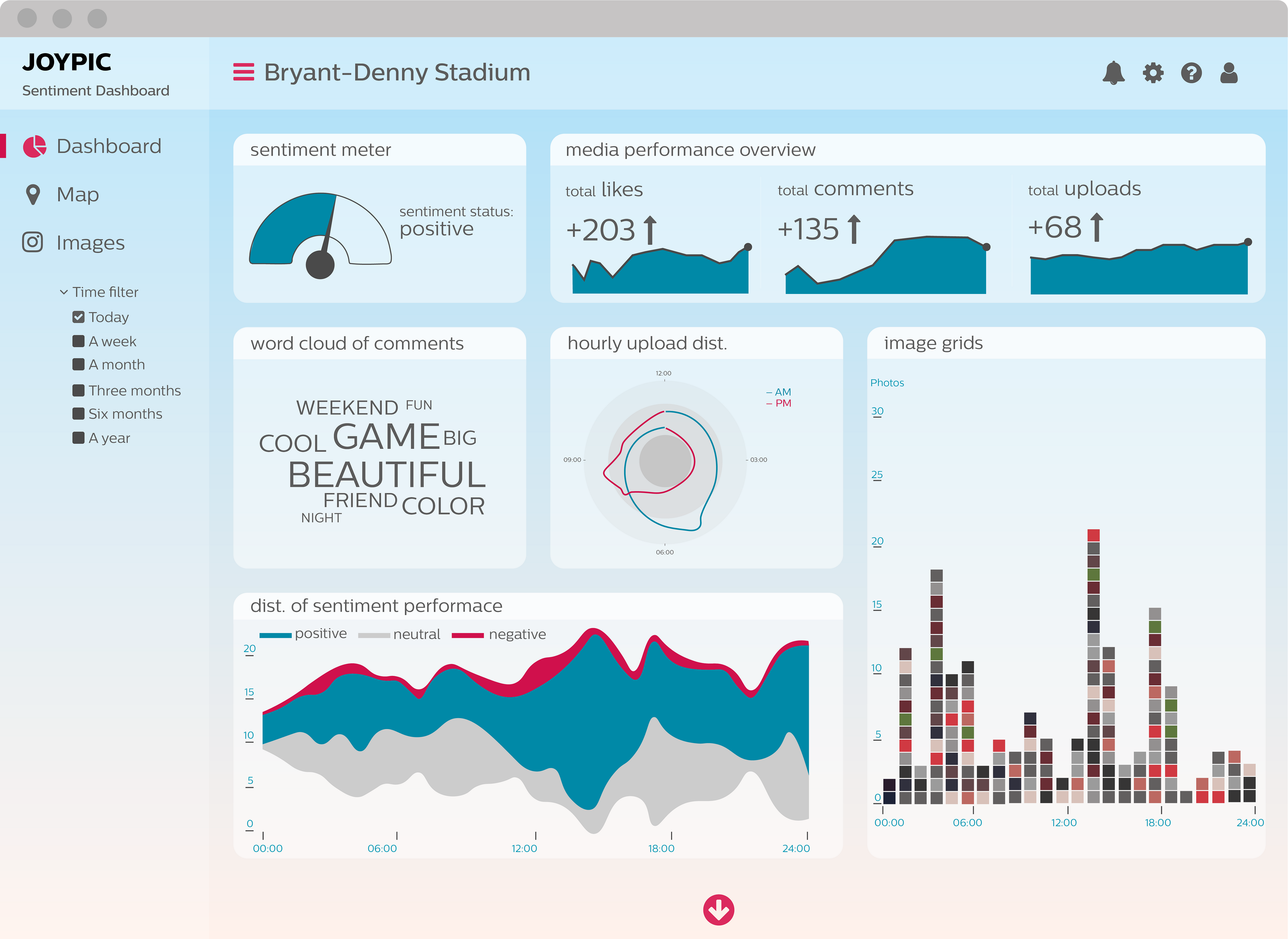
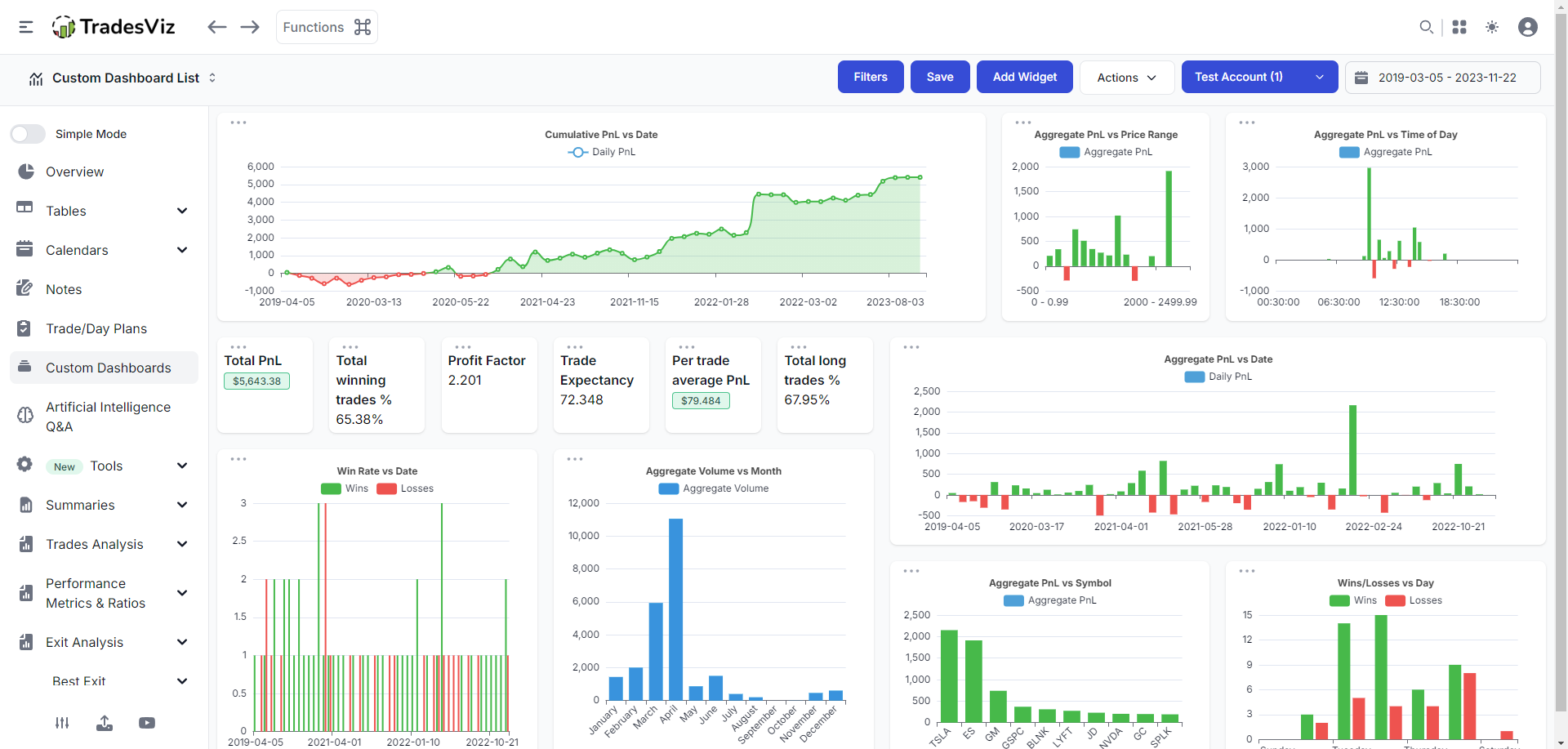
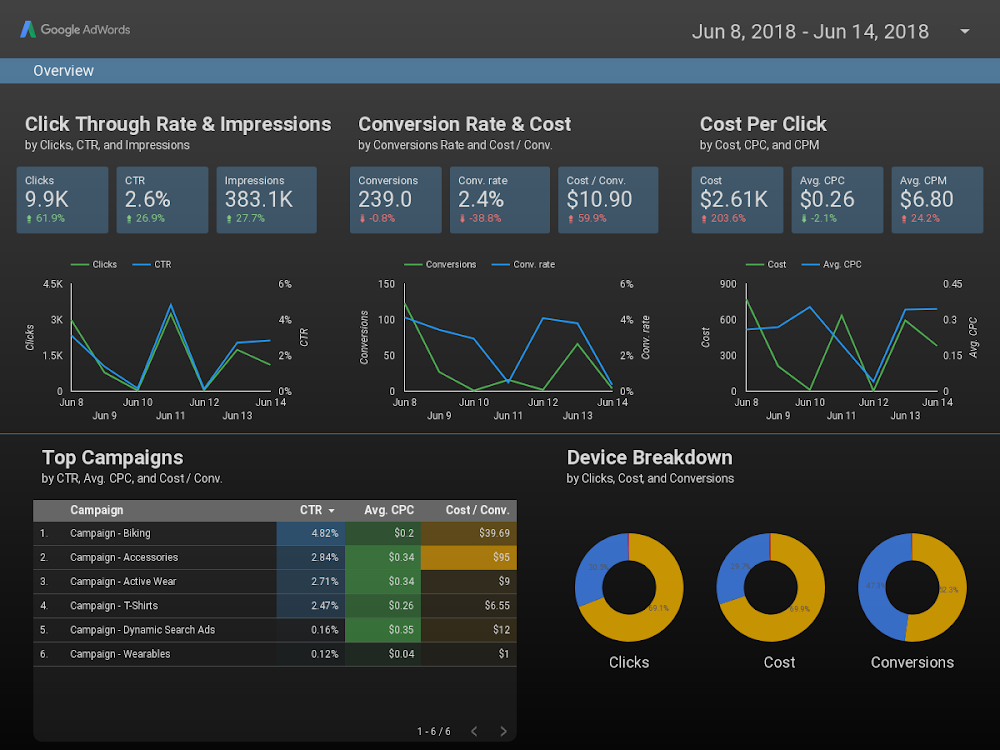
In the realm of data analysis and decision-making, a well-designed dashboard serves as a powerful tool for visualizing complex information and gleaning actionable insights. A custom dashboard, tailored to the specific needs and objectives of an individual or organization, offers unparalleled flexibility and control over the presentation and interpretation of data. This guide provides a comprehensive framework for building a custom dashboard, exploring the key elements, design principles, and best practices that ensure an effective and impactful outcome.
Understanding the Importance of a Custom Dashboard
The primary advantage of a custom dashboard lies in its ability to cater to unique requirements. Unlike pre-built templates, a custom dashboard allows for:
- Tailored Data Selection: Choosing only the relevant metrics and data points essential for informed decision-making, eliminating unnecessary clutter.
- Flexible Visualization: Employing a variety of charts, graphs, and data representations that best suit the nature of the data and the intended audience.
- Personalized Layout: Organizing information in a logical and intuitive manner, ensuring easy navigation and effortless comprehension.
- Real-time Updates: Integrating live data feeds to provide up-to-the-minute insights and facilitate agile responses to changing conditions.
The Building Blocks of a Custom Dashboard
The construction of a custom dashboard involves a structured process that encompasses several key stages:
- Defining the Purpose and Audience: Clearly articulating the goals and objectives of the dashboard, identifying the target audience, and understanding their specific information needs.
- Data Source Selection: Determining the relevant data sources, ensuring data quality and consistency, and establishing data access mechanisms.
- Metric Identification: Selecting the key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that will be tracked and displayed on the dashboard.
- Visualization Design: Choosing appropriate chart types, considering data relationships, and selecting color schemes and visual elements that enhance clarity and readability.
- Layout and Navigation: Organizing dashboard elements in a logical flow, utilizing clear labels and icons, and ensuring easy navigation and interaction.
- Data Integration and Automation: Establishing connections between data sources and the dashboard, implementing data refresh mechanisms, and automating data updates.
- Testing and Refinement: Conducting thorough testing to ensure accuracy, functionality, and user experience, and iterating based on feedback and insights.
Essential Design Principles for a Custom Dashboard
Effective dashboard design hinges on several crucial principles:
- Clarity and Simplicity: Prioritizing clear and concise communication, using minimal text and avoiding unnecessary complexity.
- Visual Hierarchy: Guiding the user’s attention to the most important information through strategic use of color, size, and positioning.
- Consistency and Coherence: Maintaining a consistent visual style throughout the dashboard, using familiar patterns and conventions.
- Interactive Elements: Incorporating interactive features like drill-down capabilities and filters to allow users to explore data in greater depth.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Designing the dashboard with accessibility in mind, ensuring it is usable by all users regardless of their abilities.
Tools and Technologies for Custom Dashboard Creation
Numerous tools and technologies facilitate the creation of custom dashboards, each offering unique features and functionalities. Some popular options include:
- Business Intelligence (BI) Platforms: Tableau, Power BI, Qlik Sense, and Looker provide comprehensive solutions for data visualization, analysis, and dashboard creation.
- Data Visualization Libraries: D3.js, Chart.js, and Plotly.js offer flexible and powerful libraries for creating custom charts and graphs within web applications.
- Spreadsheet Software: Excel and Google Sheets can be used to create basic dashboards, particularly for smaller datasets.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: Platforms like Zoho Analytics, Dundas BI, and Sisense offer drag-and-drop interfaces for building dashboards without extensive coding knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What data sources can be used for a custom dashboard?
A: Custom dashboards can leverage a wide range of data sources, including:
- Databases: Relational databases (SQL Server, MySQL), NoSQL databases (MongoDB, Cassandra)
- Spreadsheets: Excel, Google Sheets
- Cloud Services: Google Analytics, Salesforce, Amazon S3
- API Data: Data from web services and APIs
Q: How can I ensure data quality in my custom dashboard?
A: Data quality is paramount for a reliable and insightful dashboard. Consider these steps:
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to ensure data integrity and consistency.
- Data Cleansing: Cleanse data to remove duplicates, errors, and inconsistencies.
- Data Transformation: Transform data into a format suitable for visualization and analysis.
Q: What are some tips for choosing the right chart type?
A: The choice of chart type depends on the nature of the data and the message you want to convey:
- Bar Charts: Ideal for comparing discrete categories.
- Line Charts: Suitable for visualizing trends over time.
- Scatter Plots: Useful for examining relationships between variables.
- Pie Charts: Effective for showing proportions of a whole.
Q: How can I make my custom dashboard more user-friendly?
A: User-friendliness is crucial for effective dashboard use. Consider these elements:
- Clear Labels and Icons: Use clear and concise labels and icons to guide users.
- Intuitive Navigation: Design a logical and intuitive navigation structure.
- Interactive Features: Incorporate interactive elements to enhance user engagement.
- Accessibility Considerations: Ensure the dashboard is accessible to all users.
Conclusion
Building a custom dashboard is an iterative process that requires careful planning, data preparation, and design expertise. By understanding the purpose and audience, selecting relevant data sources, and applying effective design principles, you can create a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data, driving informed decision-making and achieving desired outcomes. Remember, the key to a successful custom dashboard lies in its ability to deliver meaningful insights in a clear, concise, and engaging manner, empowering users to make data-driven decisions with confidence.
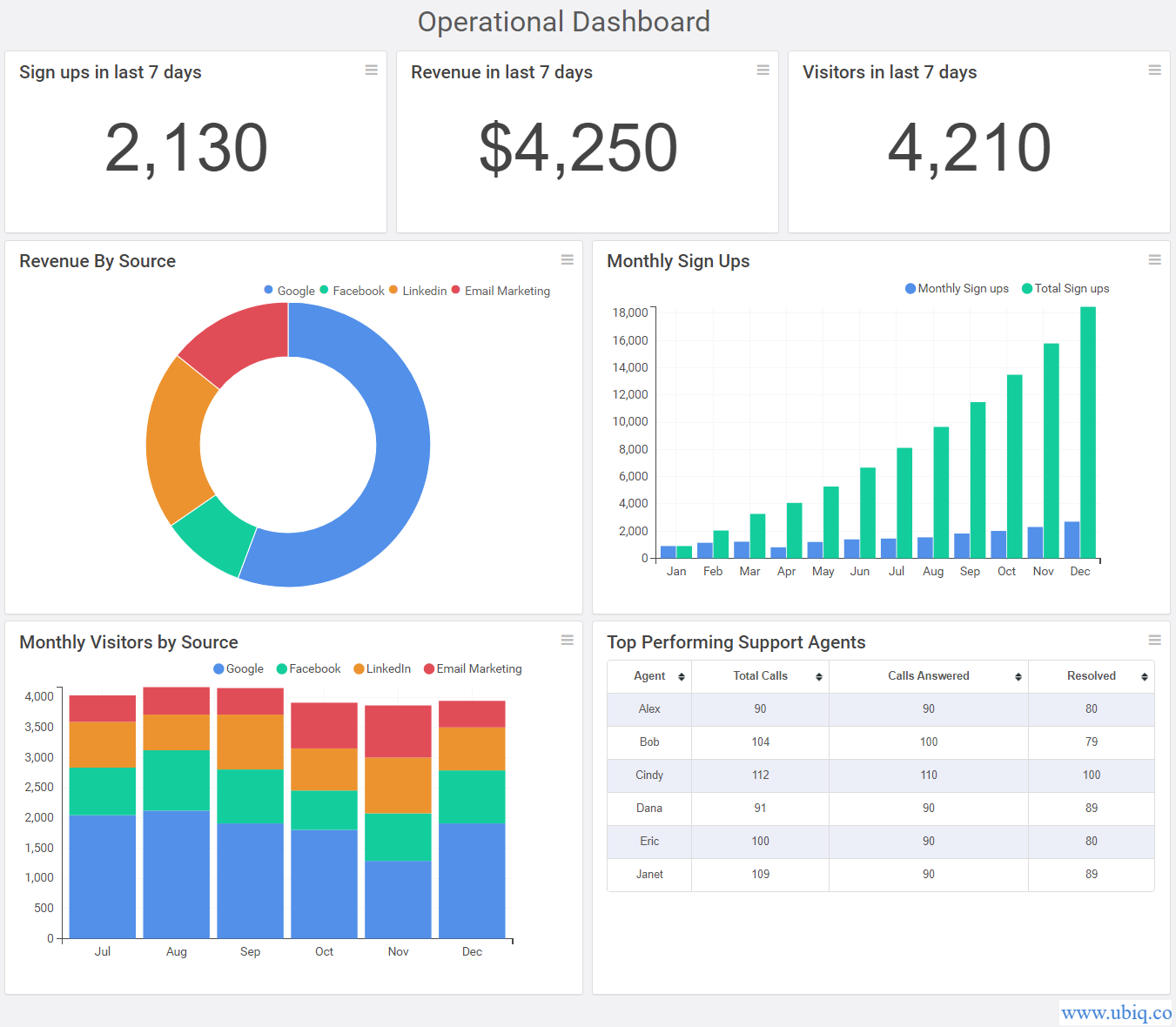
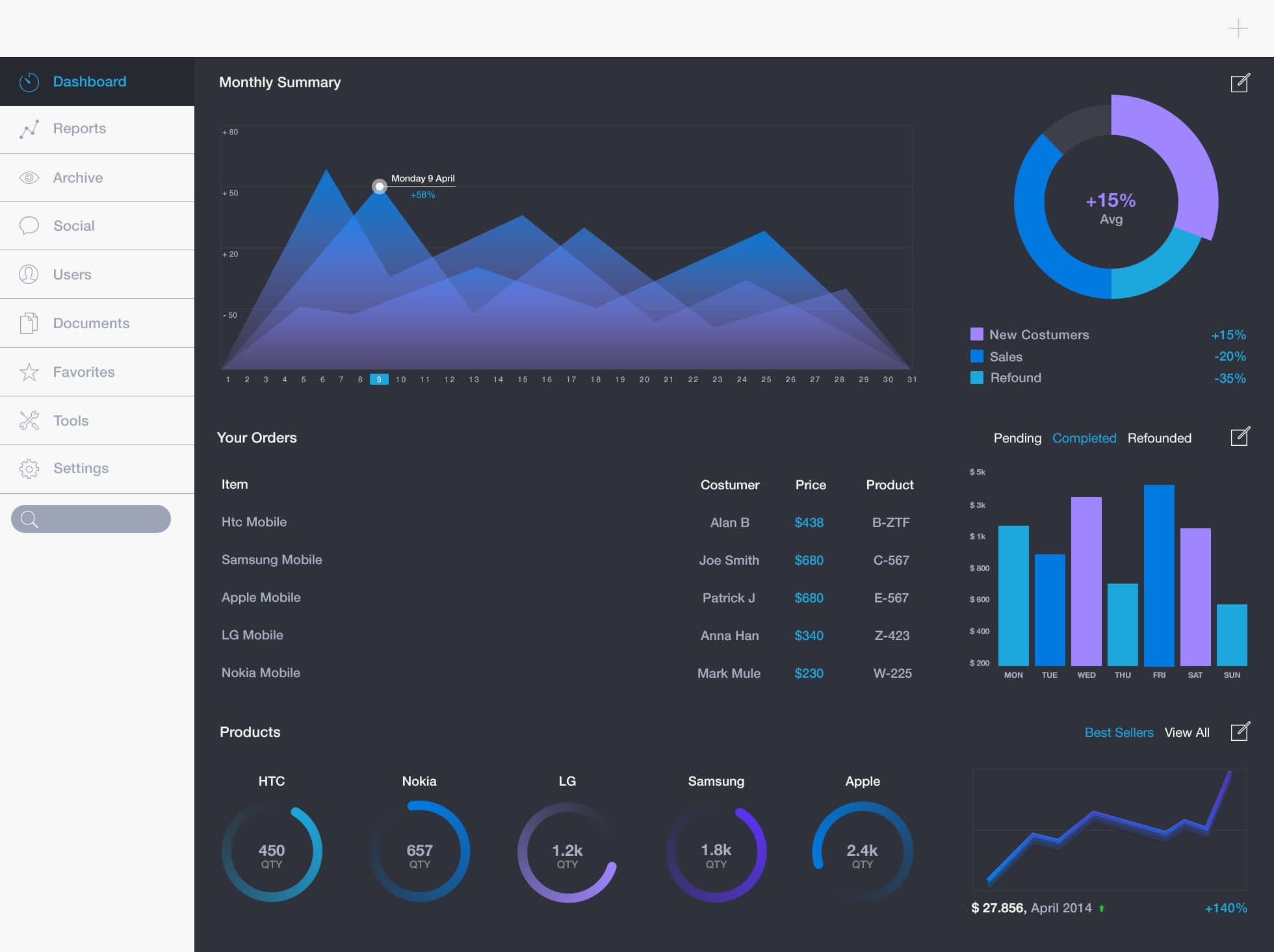



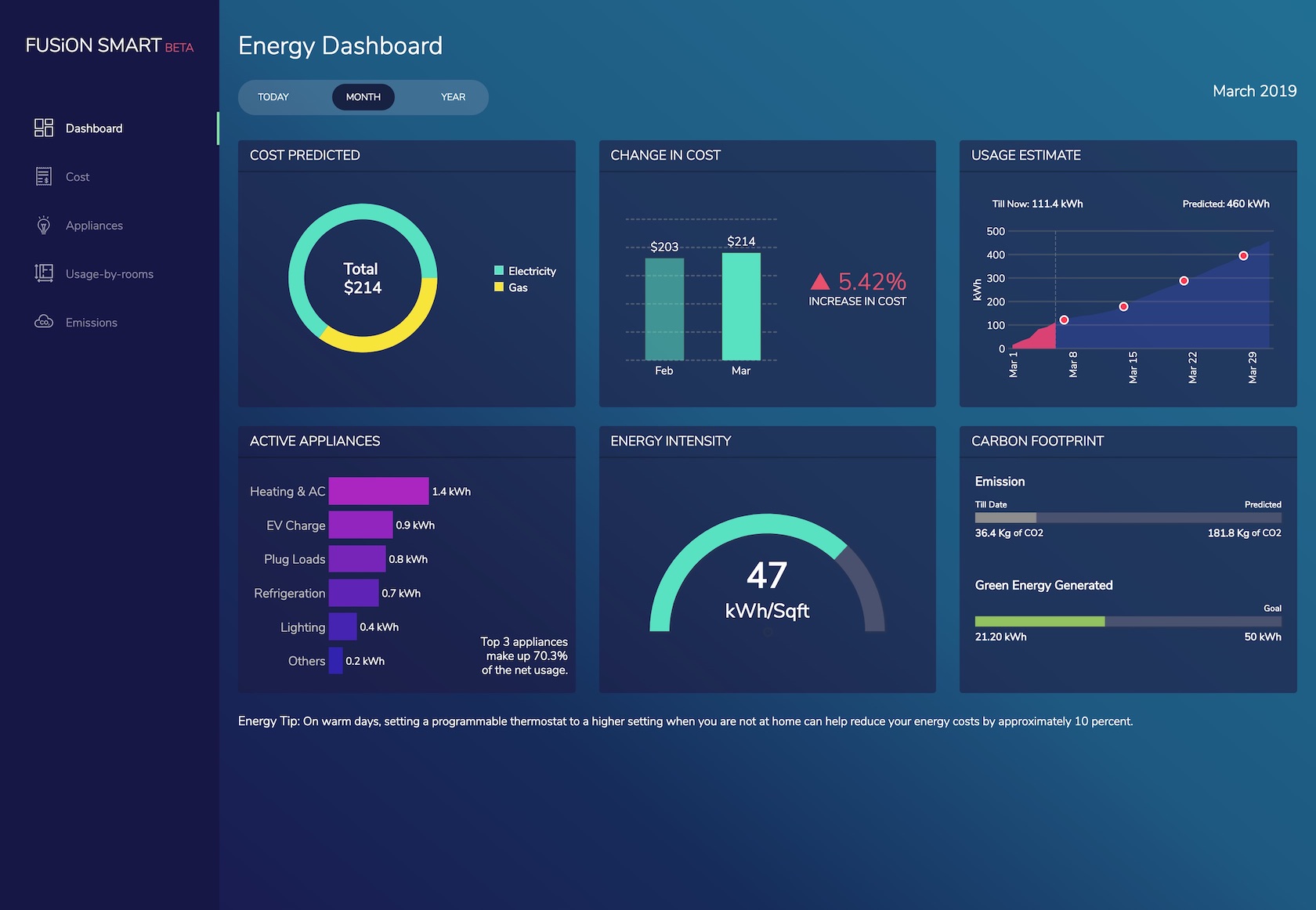
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Crafting a Custom Dashboard: A Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Your Data. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!