Building Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Building Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Building Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Building Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide
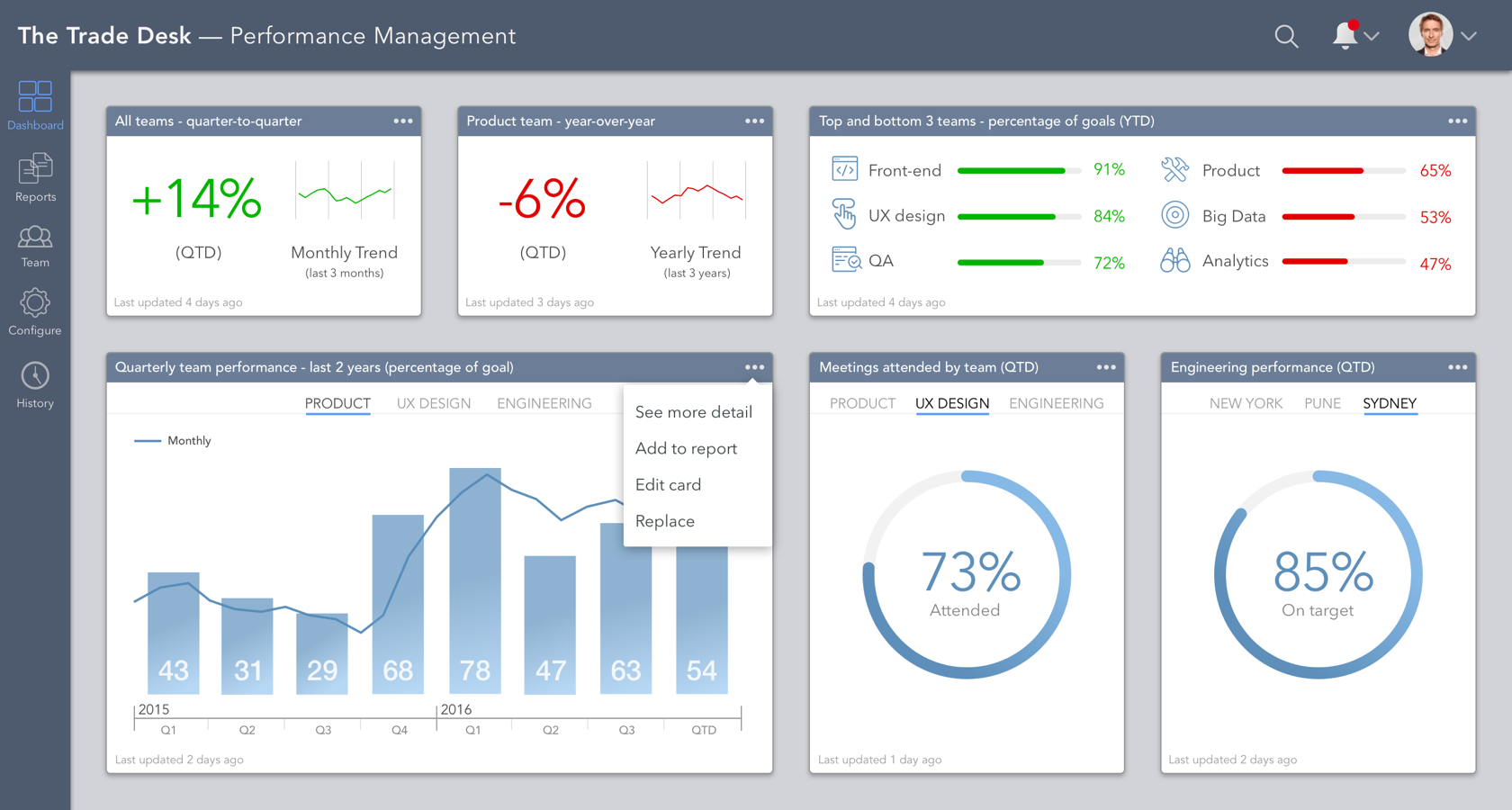
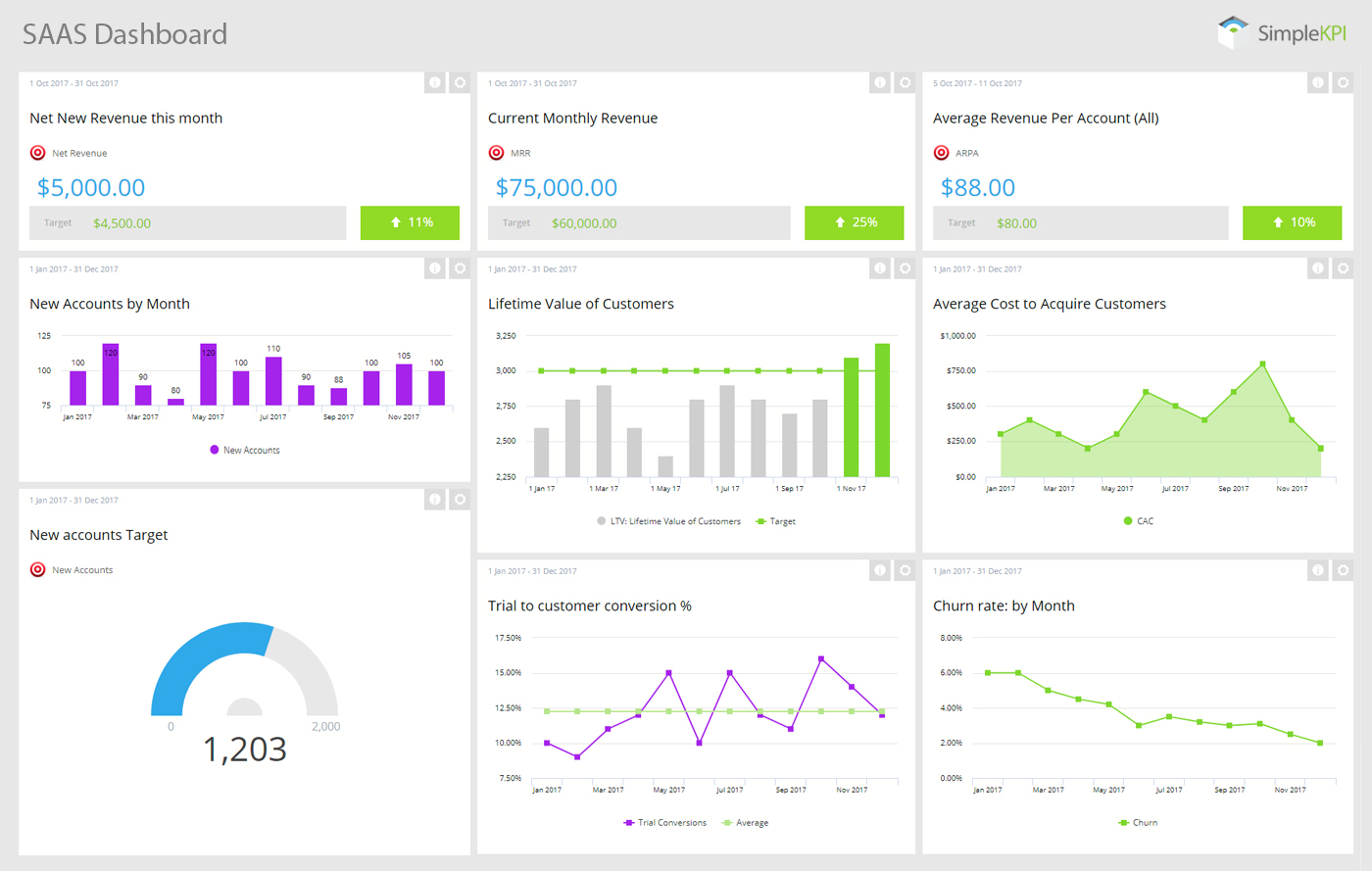
Dashboards, once considered the domain of IT professionals, have become an indispensable tool for organizations across all sectors. They provide a centralized and visually appealing platform to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track progress, identify trends, and ultimately, drive better decision-making. This guide delves into the intricacies of building effective dashboards, exploring the key principles, best practices, and tools that will empower you to create compelling visualizations that inform and inspire action.
Understanding the Purpose and Audience
The foundation of any successful dashboard lies in clearly defining its purpose and target audience. Consider these questions:
- What are the key objectives of the dashboard? Is it to track sales performance, monitor website traffic, or analyze customer behavior?
- Who will be using the dashboard? Are they executives, managers, or analysts? Understanding their needs and expertise will shape the level of detail and complexity of the dashboard.
- What specific information should the dashboard convey? Identify the KPIs and metrics that are most relevant to the intended audience and their goals.
Choosing the Right Tools and Technology
The landscape of dashboarding tools has evolved dramatically, offering a wide range of options to suit different needs and budgets. Some popular choices include:
- Business Intelligence (BI) Platforms: These comprehensive solutions like Power BI, Tableau, Qlik Sense, and Sisense offer robust data analysis, visualization capabilities, and integration with various data sources.
- Spreadsheet Software: While not specifically designed for dashboards, Excel and Google Sheets can be effective for creating simple dashboards with basic charts and graphs.
- Data Visualization Libraries: For developers, libraries like D3.js, Plotly, and Bokeh provide greater control over the design and interactivity of dashboards.
Designing for Clarity and Impact
The visual design of a dashboard is crucial for conveying information effectively and engaging the audience. Adhere to these principles:
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overwhelming users with too much information. Focus on presenting only the most important metrics and insights.
- Use Visual Hierarchy: Employ techniques like size, color, and positioning to emphasize key data points and guide the user’s attention.
- Choose Appropriate Charts and Graphs: Select visualizations that best represent the data and cater to the intended message. For example, bar charts are suitable for comparisons, while line graphs are effective for showing trends over time.
- Ensure Readability: Use clear fonts, contrasting colors, and appropriate spacing to enhance readability and avoid visual clutter.
Data Integration and Management
The quality of the data powering your dashboard is paramount. Ensure data accuracy, consistency, and timeliness by:
- Selecting Reliable Data Sources: Use trusted and validated data sources to avoid misleading insights.
- Data Cleaning and Transformation: Address any inconsistencies, missing values, or errors in the data before visualization.
- Data Refreshment: Implement automated processes to update the data regularly and keep the dashboard current.
Interactivity and Storytelling
Interactive elements can significantly enhance the user experience and provide deeper insights. Consider incorporating:
- Filters and Slicers: Allow users to drill down into specific data segments and explore different perspectives.
- Drill-Down Functionality: Enable users to access more detailed information by clicking on specific data points.
- Data Storytelling: Use annotations, tooltips, and narratives to explain trends, patterns, and insights within the data.
Testing and Iteration
Building a successful dashboard is an iterative process. Conduct thorough testing with the target audience to gather feedback and refine the design:
- Usability Testing: Evaluate the ease of navigation, understanding, and interaction with the dashboard.
- Data Validation: Verify the accuracy and consistency of the data displayed.
- Feedback Collection: Seek feedback on the effectiveness of the visualizations, the clarity of the message, and the overall user experience.
FAQs: Building Effective Dashboards
Q: What are the common pitfalls to avoid when building dashboards?
A:
- Information Overload: Avoid presenting too much data at once, leading to confusion and disengagement.
- Poor Data Quality: Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to misleading insights and undermine the value of the dashboard.
- Lack of Context: Presenting data without context can make it difficult for users to understand its significance.
- Ignoring User Needs: Designing a dashboard without considering the target audience and their needs can result in an ineffective tool.
Q: How can I ensure my dashboard is user-friendly?
A:
- Clear and Concise Labels: Use descriptive labels for axes, charts, and data points.
- Consistent Color Scheme: Employ a consistent color palette for different data categories to enhance readability.
- Intuitive Navigation: Make it easy for users to find the information they need with clear navigation menus and search functionality.
Q: What are some tips for creating engaging dashboards?
A:
- Use Visual Storytelling: Weave a narrative through the data, highlighting key trends and insights.
- Incorporate Interactive Elements: Allow users to explore the data dynamically through filters, slicers, and drill-down features.
- Tell a Story with Data: Use data to answer questions, reveal patterns, and support decision-making.
Conclusion
Building effective dashboards is not simply about creating visually appealing charts and graphs. It is about transforming data into actionable insights that drive informed decisions and improve organizational performance. By adhering to the principles outlined in this guide, you can craft dashboards that are both informative and engaging, empowering your audience to make better choices and achieve their goals. Remember, the journey of building a dashboard is iterative and requires continuous refinement based on user feedback and evolving needs. Embrace the process of experimentation and optimization to create a powerful tool that unlocks the full potential of your data.
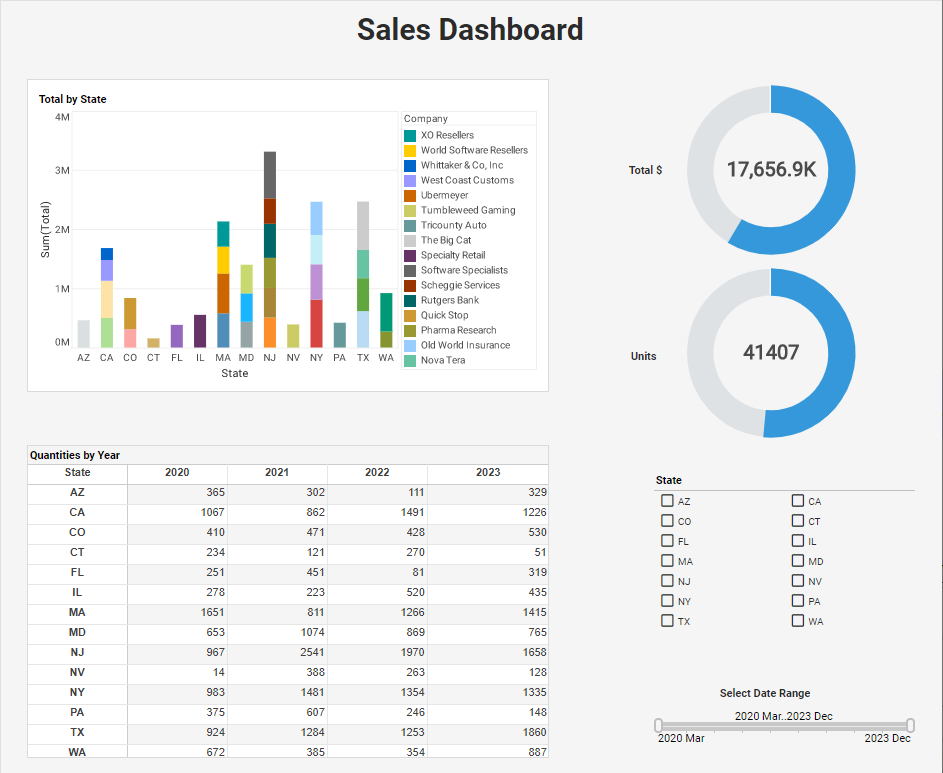
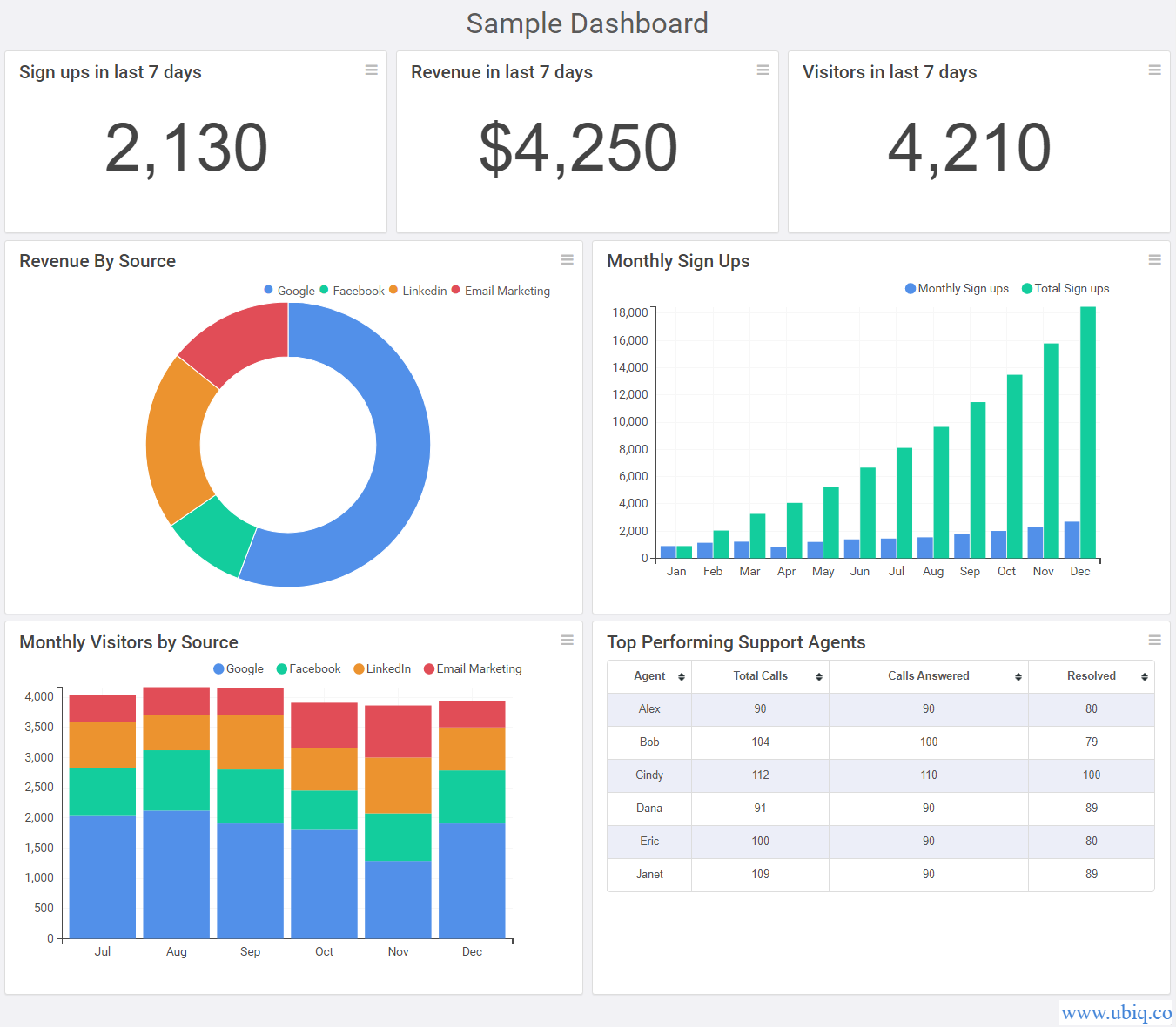



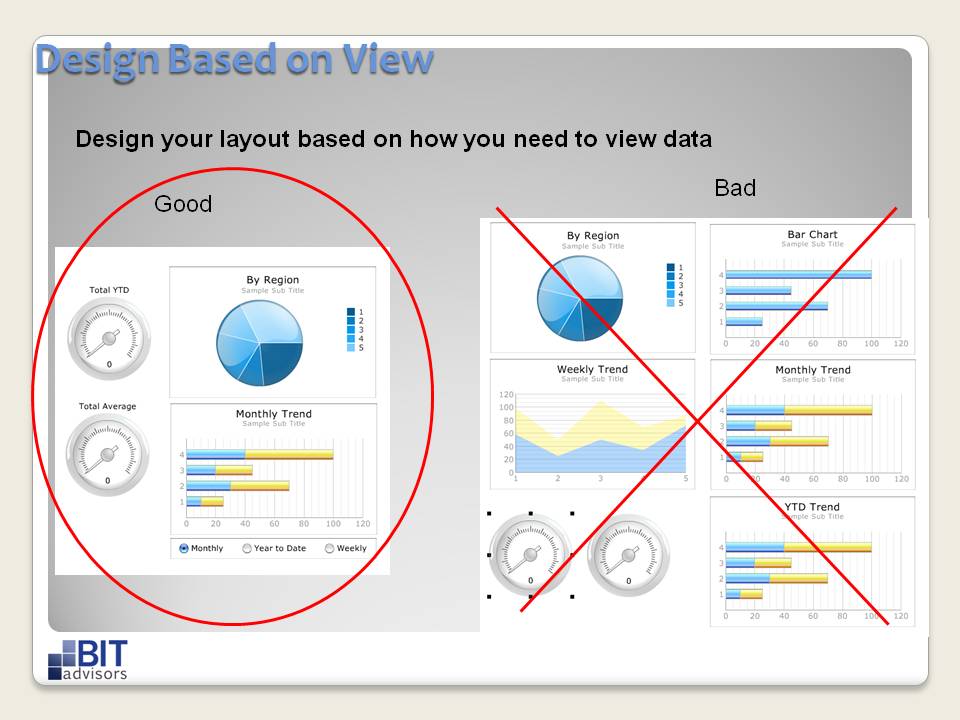

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Building Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!